WSL Setup and Networking
⚠️ Important: These instructions are for Windows 11 only. The required
mirrorednetworking mode is not supported on Windows 10.
This guide walks you through setting up a WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux) environment, installing the voyant-api configuring static IP settings in Windows, and forwarding ports to allow external UDP traffic into your WSL instance.
🐧 Install WSL2 on Windows 11
- Open PowerShell as Administrator.
-
Run the following command to install WSL (WSL2 by default) and the default distribution (Ubuntu):
wsl --installSee How to install Linux on Windows with WSL for more information.
🔗 Enable Mirrored Networking
⚠️ This is the step that is only supported on Windows 11. See Mirrored mode networking for more information.
-
Press
Windows + Rand enter:notepad %USERPROFILE%\.wslconfig -
If the file doesn’t exist, choose to create it.
-
Add the following content:
[wsl2] networkingMode=mirrored -
Save the file (Ctrl + S).
🚀 Start WSL
Launch the Ubuntu (or other) app from the Start Menu.
📦 Install the Latest voyant-api Release
-
Download packages from voyant-sdk/releases/latest
-
Copy files from your Windows Downloads folder into your WSL home directory:
cp /mnt/c/Users/<YOUR_USERNAME>/Downloads/voyant-api*.deb .Replace
<YOUR_USERNAME>with your actual Windows user folder name. -
Install the packages:
sudo apt update sudo dpkg -i voyant-api*.deb -
Fix any missing dependencies (if needed):
sudo apt --fix-broken install -
Verify your installation, by running:
voyant_hello_world
And you should see something like:
Welcome to the Voyant Photonics, Inc. API!
You have successfully installed the voyant-api package with:
- Proto version: 0.2.1 (Proto)
- API version: 0.2.1 (API)
🌐 Set Up Ethernet Adapter (Static IP)
On your Windows machine, configure your Ethernet interface with a static IP that will be used for port forwarding. Select Edit on the IP assignment in your ethernet interface’s settings.
Example Settings:
- IP address:
192.168.20.100(This will be<YOUR_WINDOWS_STATIC_IP>below) - Subnet mask:
255.255.255.0 -
Gateway: (Leave blank)
-
Ethernet adapter not connected / interface details
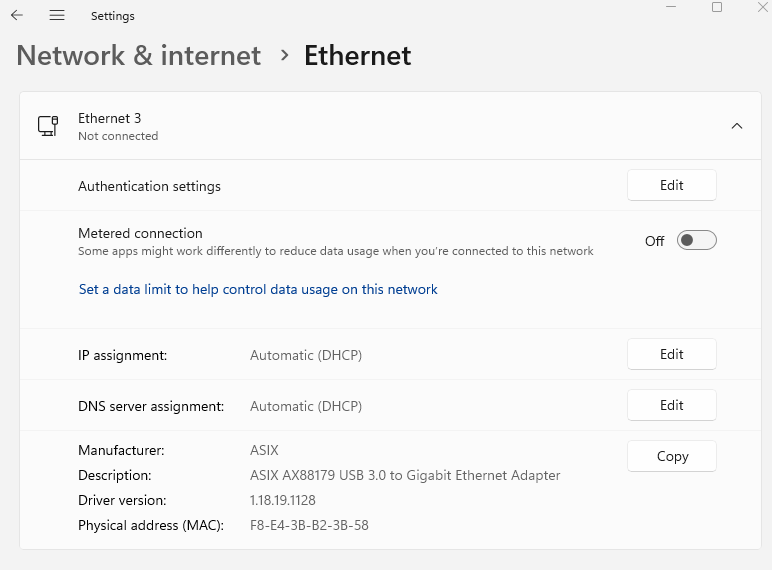
-
Static IP configuration dialog (Manual)
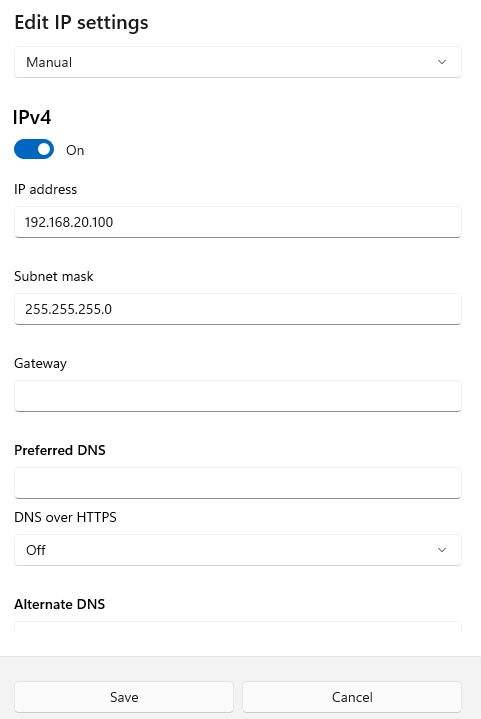
-
Confirmation of manual IP set
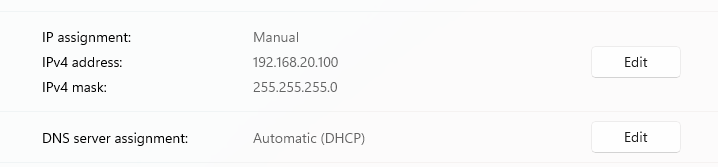
You can now ping your device in both a PowerShell and a WSL terminal with:
ping 192.168.20.20
🔍 Get Your WSL IP Address
In your WSL terminal, run:
ip addr show eth0
Look for an IP address in the format 172.x.x.x (e.g., 172.22.147.139). This is your WSL instance’s internal IP address (<YOUR_WSL_IP>).
🔀 Set Up Port Forwarding (UDP)
Forward UDP port 4444 from Windows to your WSL instance.
- Open PowerShell as Administrator.
-
Run the following command:
netsh interface portproxy add v4tov4 listenport=4444 listenaddress=<YOUR_WINDOWS_STATIC_IP> connectport=4444 connectaddress=<YOUR_WSL_IP>Replace:
<YOUR_WINDOWS_STATIC_IP>→ your Windows static IP (Likely192.168.20.100)<YOUR_WSL_IP>→ your WSL internal IP (172.x.x.xfrom previous step)
🔓 Allow UDP Through Windows Firewall
Run this command to allow UDP port 4444 through the firewall:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="WSL UDP 4444" dir=in action=allow protocol=UDP localport=4444
🛠️ Troubleshooting
If you see the following error:
Error: No such device (os error 19)
then you are failing to open the UDP socket. This means the port forwarding / firewall is not properly configured.
First try restarting the WSL instance by shutting it down:
wsl --shutdown
and relaunch your WSL instance.
If this doesn’t work, evaluate your networking configuration and reach out to us at Troubleshooting Guide.
✅ Next steps
You are now setup to run the voyant-api through WSL. Please refer to the latter half of the Quickstart Guide to start your sensor, visualize point cloud data, record data, etc.